 As an artist or painter, one of your most important decisions is how and where to create your work. While canvas is a common choice among painters, not all surfaces are created equal, and it can be confusing to understand which type of canvas is right for your project.
As an artist or painter, one of your most important decisions is how and where to create your work. While canvas is a common choice among painters, not all surfaces are created equal, and it can be confusing to understand which type of canvas is right for your project.
Whether you are a water-colorist or an oil painter, understanding the basics of “canvas” will give you the insights needed to choose the right option and get started on your masterpiece. This article covers everything from what types of materials make up the canvas to how exactly paint should be applied and tips for caring for your artwork after it’s finished.

Let’s take a deep dive together into all aspects surrounding this – from understanding different types of canvases available on the market today, key steps involved in preparing a canvas before getting started with painting, understanding priming and stretching processes associated with creating any kind of art on another surface besides traditional paper – it’s all here!
What is Canvas Exactly? Understanding The Basics Of Canvas for Art
Canvas is a plain-woven fabric that is known for its durability and strength. It is usually made out of cotton, but linen can also be used to create the material. Canvas has many practical uses, from painters using it as their canvas to handbag designers creating stylish bags with the fabric. Sailors even use canvas for sails and other items on boats due to its heavy-duty nature.
How is Canvas Made?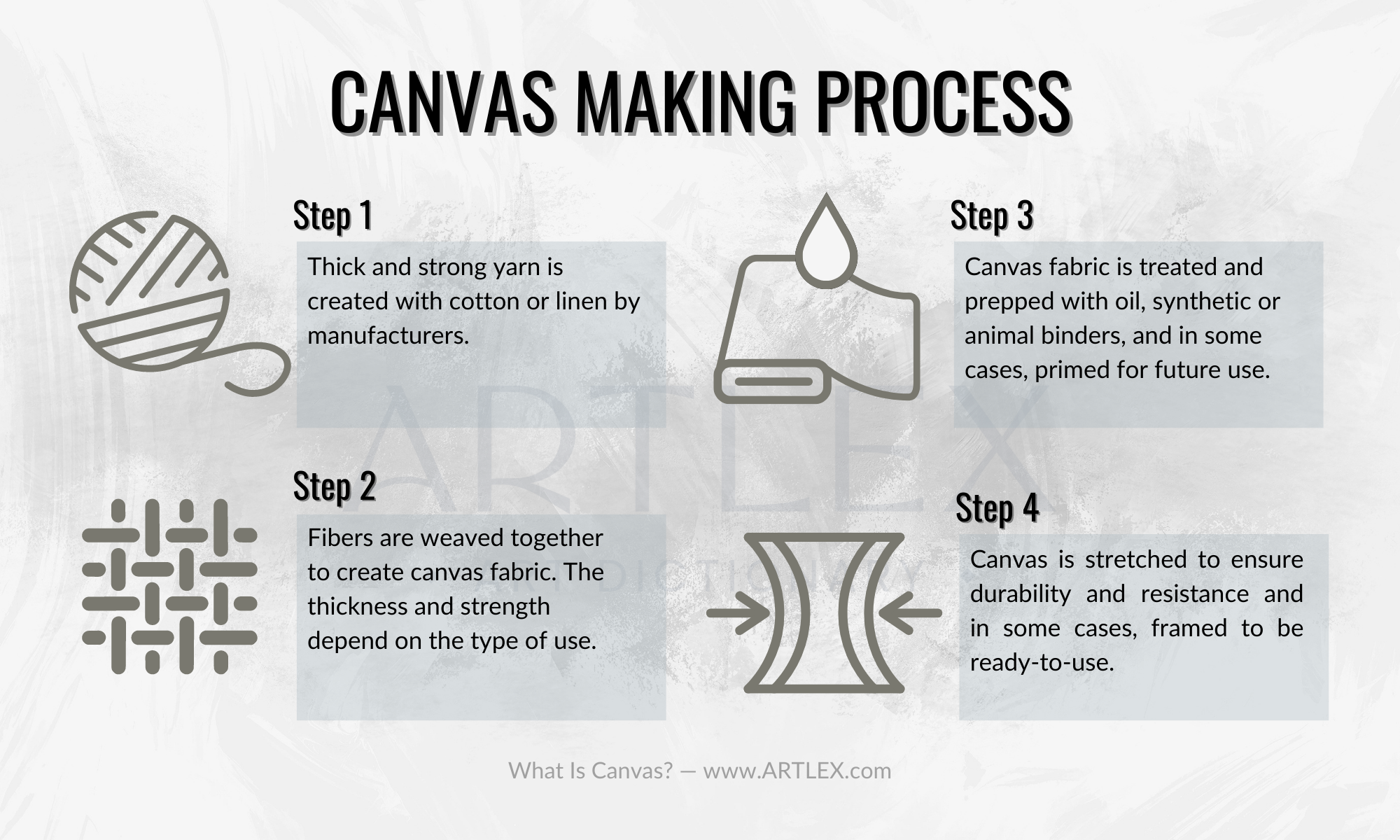
The process of making canvas involves weaving together two sets of yarns in order to create a strong material that will last through wear and tear. The warp yarns are woven over and under each other, while the weft yarns are woven in alternating patterns. This creates a sturdy fabric that can withstand harsh conditions such as wind or water without breaking down easily. The thickness of the weave determines how durable it will be; thicker weaves result in stronger fabrics, while thinner ones may not hold up as well over time.
In addition to being durable, canvas also offers several other benefits. Its thick weave makes it resistant to punctures and tears, meaning items made from this material will last longer than those made from thinner fabrics like silk or satin or thinner materials like paper, which may rip more easily when exposed to sharp objects.
The rough surface of canvas means that paint will adhere well to it, making it an obvious choice for most art mediums.
Different Types Of Canvas Materials
There are various types of canvas available, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits.
Cotton Canvas
Cotton is the most common type of canvas used by artists due to its affordability and availability. It is relatively lightweight and provides a good surface for painting on.
Linen Canvas
Linen canvas is another popular choice among professional artists due to its superior quality compared to cotton canvases. Linen canvas fabric has a stiffer texture than cotton but can be more expensive depending on the grade of linen used in production.
Types Of Canvas Surfaces
Canvas can also be classified according to the preparation process it went through. Some canvases that are better fit for certain mediums, like oil painting, pass for a different preparation process that makes the ideal and more resistant to the medium and possible dissolvents and chemicals used with it.
Oil Canvases
Oil canvases are specifically designed for use with oil paints. They have a special priming treatment that makes them resistant to possible canvas degradation caused by oil paintings, while absorbent canvases are intended mainly for tempera paint applications.
- Priming: The canvas is prepped with an oil-based primer to create a smooth surface and prevent the oil paint from soaking into the canvas. This is an important step to ensure the longevity of the painting. You can always use gesso or other priming mediums afterward.
- Drying: The primed and sanded canvas is allowed to dry completely before painting begins. This can take several hours or even days, depending on the conditions. Oil canvases need to be completely air dry, while other canvases can be dried in a hot air oven.
- Sanding: The surface of the primed canvas is sanded to create a smooth surface and remove any bumps or rough spots. Since the base coat is already applied, you can also repeat this step with normal priming mediums like acrylic gesso.
- Stretching: The canvas is stretched over a wooden frame, known as a stretcher bar, to create a flat and tight surface for painting. This is a process you can also do yourself, and it helps to prevent the canvas from sagging or wrinkling as the paint dries.
Universal Canvases
Universal canvases offer versatility in that they can be used with oil paints and acrylics, making them ideal for those who work in multiple mediums or want to experiment with different techniques without purchasing multiple types of canvas materials.
Canvas Treatments
No matter what type of artist’s canvas you choose, all will have been given some sort of treatment after the production processes. These treatments, such as priming or sizing, help protect the fabric from damage caused by moisture or other environmental factors like UV light exposure over time.
Priming Treatment
Priming involves applying one or more layers of primer onto the surface before beginning your artwork; this helps create an even base layer that allows colors applied later on top look brighter and sharper when finished.
Sizing Treatment
Sizing also adds protection against moisture absorption which could cause warping or buckling if left untreated; this usually consists of either animal glue (hide glue) , starch-based paste, synthetic polymers (acrylic emulsions) , waxes, oils etc., depending on the desired effect needed.
Characteristics of Canvas Brands
The weight/thickness/texture/stretchability/durability etc., of each type varies significantly between brands so it’s important that you do your research first before committing yourself into buying any particular kind – especially if you plan on using it professionally! For example, lighter-weight fabrics tend not to hold up well under heavy brushwork, whereas heavier ones may require additional supports like stretcher bars when stretching them out prior to working on them. Similarly, stretchable fabrics might be better suited for larger works where precise control over tension levels needs to be maintained throughout long periods. In contrast, non-stretchable ones would fare better when dealing with smaller pieces where accuracy isn’t necessarily required at every stage during the creation process.
There are many different types of artist’s canvas available today – each offering its own unique advantages depending upon what kind of artwork they’re being utilized within! As such, it’s important that anyone looking into purchasing some should take time researching beforehand, so they know exactly what qualities best suit your needs.
Preparing A Canvas For Painting
Preparing a canvas for painting is an important step in the artistic process. Gesso is the preferred choice for priming and sealing a canvas before painting. It is available in white or colored varieties and various consistencies depending on the desired effect. A thicker consistency creates a textured surface, while thinner layers provide smoother results. Applying gesso should be done with either a 1″ – 2″ flat brush or sponge to ensure even coverage of the entire canvas front and sides. This helps to prevent the warping of the material over time due to uneven application of paint or other materials later on in the process.
When applying gesso, it’s important to work in thin layers and allow each layer to dry completely before adding another coat; this prevents buildup that can cause cracking down the line when exposed to moisture or other environmental factors such as temperature changes. Additionally, it’s essential that you apply gesso with strokes going along with the fibers of your chosen material; this ensures that no cracks form between them during drying periods which could lead to further damage down the line, during use, or transport from one location to another.
Once all coats have been applied and dried thoroughly, sanding with fine grit sandpaper can help create an even smoother surface prior to beginning any painting projects on top of it; this also helps remove any small bumps created by air bubbles trapped underneath multiple coats of gesso which would otherwise remain visible after completion if not taken care off beforehand properly. Finally, ensure you are working in a well-ventilated area since fumes from freshly applied gesso can become pretty intense if left without proper ventilation.
Following these steps will ensure your canvas has been prepped properly before beginning any artwork project. Taking extra time at this phase may seem tedious, but it ultimately pays off later down the road.
Understanding The Canvas Priming Process


The canvas priming process is a critical step in the creation of a painting on canvas. Priming prepares the surface of the canvas for painting, prevents the paint from soaking into the canvas fibers, and creates a suitable surface for the paint to adhere to. This process is performed by artists themselves or in a commercial setting by specialized canvas businesses.
Commercial priming operations use high-quality primer materials and modern equipment to achieve consistent results. This can be especially useful for artists who need large numbers of primed canvases, as the initial steps of the process can be time-consuming and difficult to achieve with the same level of precision and uniformity as in a commercial setting. However, many professional artists prefer to do this process on their own and have developed unique priming techniques to create specific textures, colors, and other visual effects.
The priming process significantly affects the canvas’s resistance to various environmental factors such as moisture, heat, and light. A properly primed canvas is less likely to degrade over time, allowing the painting to maintain its appearance for many years.
When using acrylic sizing, it is applied as the first step on raw canvas, followed by applying acrylic gesso as the second step. This process limits the canvas’s absorbency and helps with the paint film’s adhesion to its primed surface. The color relationship between your primed surface and the colors used in your work should also be taken into consideration when priming since this will affect how vibrant or dull they appear on the finished product.
The importance of priming in the art world has been recognized for centuries. Throughout history, artists have used various priming materials to create the desired surface for their paintings, from simple animal-skin glue to modern synthetic materials.
It’s important to understand that each material has its own properties, so selecting one over another depends entirely on what kind of effect you’re aiming for with your painting project – whether it be smoothness or texture – so make sure you do some research before deciding which primer works best for you!
What Paints To Use On Canvas
When it comes to painting on canvas, acrylic paint is the most popular choice. It is easy to work with and dries quickly, making it ideal for a variety of art projects. A primed canvas provides an optimal surface for applying acrylic paint with either a brush or palette knife. When starting out, the type of paint used will depend largely on the desired outcome and level of experience.
Acrylic Paints
Acrylic paints are water-based and come in a wide range of colors, including bright hues that can be mixed together to create unique shades. They also have excellent adhesion properties which make them perfect for use on canvas as they won’t flake off over time like some other types of paints can do when applied directly onto unprimed canvases. Acrylics also dry very quickly so there’s no need to wait long periods between layers or coats when creating artwork on canvas using this medium.
Need to find a good oil paint for your canvas? See our yearly guide on the Best Acrylic Paints!
Oil Paints
In addition to acrylics, oil paints are another popular choice for painting on canvas due to their ability to produce vibrant colors that last longer than those created by other types of paint, such as watercolors or tempera paints, which tend to fade over time, unlike oils. Oils take much longer than acrylics to dry. Still, they offer more flexibility in terms of blending colors together and creating subtle gradations in tone or hue within one piece of artwork thanks to their slow-drying nature, which allows artists plenty of time to blend different tones before each layer sets completely.
Need to find a good oil paint for your canvas? See our yearly guide on the Best Oil Paints!
Gouache Paints
Finally, gouache is another option available if you’re looking to create something special for your next project. This opaque watercolor-like medium offers great coverage while still allowing light through its pigment particles, resulting in brighter hues than traditional watercolors might achieve. Gouache also has good adhesion properties, so it won’t flake off after being applied onto primed canvases like some other paints may do without a primer first.
Overall, any of these three options: acrylics, oils, and gouache, could be suitable depending on what kind of effect you want to achieve in your final artwork.
Techniques For Painting On Canvas
Canvas has long been the preferred surface for painting and is great for exploring a wide range of techniques. From traditional oil painting to modern acrylic techniques, canvas offers endless possibilities for artists to express their creativity. In the following section, we’ll list some of the most comon painting techniques on canvas, including impasto, dry brush, and glazing.
Whether you’re a seasoned painter or just starting out on your art journey, these techniques are a solid starting point and will provide a strong foundation for you to build upon.
- Wet-on-Wet: This painting technique involves applying paint to a wet canvas or onto diluted paint for blending and mixing colors easily. This technique is great for creating soft gradients and fluid effects.
- Pouring: This technique involves pouring diluted or thin acrylic paint onto the canvas to create a fluid and organic effect. It is often used to create abstract paintings and “process” art.
- Impasto: Impasto is a technique where thick layers of paint are applied to the canvas to create textured and three-dimensional effects. This technique is typically made with oil or acrylic paint and a palette knife, and the paint is applied in thick, heavy strokes. Heavy body gesso is also used for this technique since it allows the artist to add a first layer of texture that can be difficult to achieve with paints only.
- Dry Brush Painting: Dry brush painting involves using a dry brush to apply paint directly to the canvas, creating rough and textured strokes. This technique is often used to create an “aged or weathered” effect, and it’s particularly useful for abstract painting, landscape painting, and creating textures or fur.
- Glazing: Glazing is a painting technique where thin layers of transparent, diluted paint are applied over a base layer to create depth/add color and luminosity. The layers of glaze allow light to penetrate and reflect off the surface, giving the painting a glowing effect. This technique is often used in oil painting but can also be done with acrylics.
Finishing A Painting On Canvas
Finishing a painting on canvas is an important step in the creative process. It requires careful consideration and attention to detail, as it can make or break the overall look of the artwork.
After the painting process is complete, several steps must be taken to finish a painting on canvas properly. Edgework is one of the first considerations, as it gives the painting a finished appearance and protects the edges from damage to a certain degreee. Options for edge work include painting the edges the same color as the background, covering the edges with a solid color, or creating a decorative border around the edge of the canvas.
The next step in the finishing process is varnishing, which protects the paint surface from dust, dirt, and UV light. Varnishing also provides a protective barrier that helps the colors to remain bright and vivid over time. Different types of varnish are available for different art mediums like oils, acrylics, etc. It is important to choose the right type of varnish for the painting medium and to apply it correctly to ensure that it does not damage the paint or alter the appearance of the colors.
When it comes time to declare a painting finished, it is up to the artist’s discretion, as no further work should be required at this point. After signing and naming their masterpiece, they should photograph it for future reference and record all details regarding its creation, such as materials used, date of creation, etcetera.
After the varnish has dried, the painting should be stored properly to protect it from damage. You should store it in a dust-free environment, keeping it away from direct light and heat, and taking extra steps, to prevent it from becoming wet or otherwise damaged by humidity or mold.
Tips For Caring And Storing Your Canvas Art

Proper care and storage are essential to preserving the beauty and integrity of your art for years to come. Here are some tips to help you care for and store your art:
- Clean Regularly: Dust and grime can build up on the surface of your canvas art, so it is essential to clean it regularly. Use a soft, dry cloth to gently wipe the surface, being careful not to rub too hard or damage the paint. You can use a damp cloth with a mild or neutral detergent for more stubborn stains.
- Avoid Exposure to Sunlight: Direct sunlight can cause fading and discoloration of the paint’s pigments over time, so it is best to avoid exposing it to direct sunlight whenever possible. If you must display your art in a sunny room, consider using window treatments to reduce the amount of direct sunlight that reaches the art.
- Maintain a Stable Environment: Canvas can be sensitive to fluctuations in temperature and humidity, so it is important to store it in a stable environment. This means avoiding damp or humid areas and keeping the temperature and humidity levels as consistent as possible.
- Use Acid-Free Materials: When storing or displaying your canvas art, use acid-free materials whenever possible. This includes matting, framing, and storage containers. Acidic materials can cause discoloration and deterioration of the canvas fabric and paint over time.
- Store Carefully: When storing your canvas art, wrap it in acid-free paper, parchment paper, or a protective wrap to prevent dust and damage. Store it in a dry, cool place, away from direct light and heat, don’t forget to protect the corners as well!
- Handle With Care: When handling your canvas art, be gentle and avoid excessive handling. Use two hands to support the painting, and avoid leaning it against walls or other surfaces that could damage the edges.
By following these tips for caring for and storing your canvas art, you can help ensure that your art remains beautiful and in good condition for many years.
If you’re looking for even more security when storing canvas paintings, consider self-storage units where they can be kept away from dust particles and other elements that could potentially harm them over time. Professional art handlers may also be able to provide additional advice on how best to store canvases safely depending on their size and shape; they may even offer wrapping services using cloths specifically designed for protecting artwork during transport or storage periods too! Finally, don’t forget about labeling all boxes of artwork with tape labels along with creating written records of what has been stored where – this way, you’ll always know exactly what pieces are located at any given moment without having to search through multiple containers!
What are Canvas Prints?
Canvas prints are commercially made art prints or photo prints that print directly onto a canvas, usually via a process called Giclee printing, or inket printing. Canvas prints are a popular option for art reproductions, home decor, and photo prints.
If you are interested in using canvas prints to reproduce your art, print your photography, or for home decor or any other purpose, you can consult our yearly guide on the Best Canvas Prints.
Conclusion
Canvas has been a primary tool for artists for hundreds of years, and as an aspiring artist, it’s essential to know the fundamentals of the material. The above article covered aspects of canvas for painting, including what it is, how it’s made, the types of canvas, and tips on priming and storage of canvas art.
We hope you enjoyed this article!

